Carbon Filtration Technology
Our ductless fume cabinets incorporate our exclusive Multiplex™ high performance activated carbon filters, which are the primary filtration component in removing all chemical fumes from within our products before the air is recirculated into the laboratory.
Activated carbon exhibits excellent adsorbent characteristics that make carbon useful for a wide variety of processes, including filtration, purification, deodorization, decolorization, purification and separation.
The effectiveness of activated carbon as an adsorbent is attributed to its unique properties, including “large surface area, a high degree of surface reactivity, universal adsorption effect, and pore size.”
Activated carbon is produced from a wide variety of carbon-rich raw materials, including wood, coal, peat, coconut shells, nutshells, bones and fruit stones. New materials are currently under investigation as sources for activated carbon.
The two primary types of activation are:
- Chemical Activation
- This technique is generally used for the activation of peat and wood-based raw materials.
- The raw material is impregnated with a strong dehydrating agent, typically phosphoric acid or zinc chloride mixed into a paste and then heated to temperatures of 500 – 800°C to activate the carbon.
- The resultant activated carbon is washed, dried and ground to powder.
- Steam Activation
- This technique s generally used for the activation of coal and coconut shell raw material which is usually processed in a carbonized form.
- Activation is carried out at temperatures of 800 – 1100°C in the presence of steam.
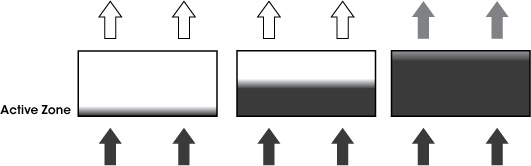
Filter Monitoring
There are two aspects to filter monitoring:
- Checking the airflow to ensure the pre-filter is not clogged with dust.
- Checking the exhaust air for chemical contaminants to ensure the main filter has not reached the breakthrough point.
Airflow can be measured with an anemometer. There are a number of anemometer designs available including propeller, hot wire and vane anemometer. In addition, most ductless fume hoods are fitted with a low airflow alarm which indicates a low airflow situation as well as fan failure.
Air Science uses high-quality centrifugal fans to ensure that airflow is maintained even as the pre-filter airflow resistance increases. Filter monitoring should aim to detect the period of initial breakthrough and in all cases should warn the operator well before the permissible exposure level (PEL) is reached.